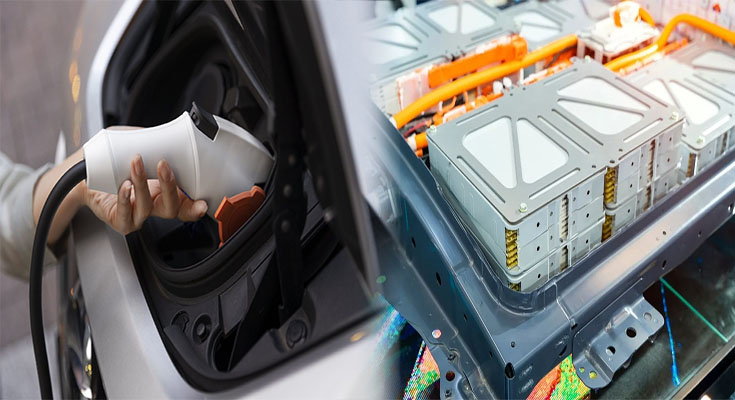
Exploring Different Chemistries in Electric Car Battery Packs
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular as a clean and efficient mode of transportation. One of the key components that determine the performance and range of an electric car is its battery pack. Within the battery packs, different chemistries are employed to store and discharge energy. In this article, we will explore some of the different battery chemistries used in electric car battery packs and their characteristics.
1. Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used chemistry in electric car battery packs. They offer a high energy density, allowing EVs to achieve longer ranges on a single charge. Li-ion batteries also have a relatively low self-discharge rate and are known for their power density, which enables electric cars to accelerate quickly.
Lithium-ion batteries come in various configurations, such as Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO2), Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4), and Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC). Each configuration has …
Exploring Different Chemistries in Electric Car Battery Packs Read More